XAMPP is a free and open-source software package that provides an easy way to set up and run a local web server environment on various operating systems, including Ubuntu.
The acronym stands for Cross-Platform (X), Apache (A), MySQL (M), PHP (P), and Perl (P), representing its core components. XAMPP is especially useful for web developers as it includes all the essential tools required to develop, test, and debug web applications in a local environment before deploying them to a live server.
On Ubuntu, XAMPP simplifies the process of managing a web server by packaging Apache, the popular HTTP server, alongside MySQL (or MariaDB in recent versions) for database management and PHP/Perl for server-side scripting. These components are configured to work together seamlessly, eliminating the need for manual configuration and reducing potential compatibility issues. Once installed, XAMPP can be started and managed from the terminal or a graphical control panel, providing control over the running services and allowing developers to enable or disable Apache, MySQL, and ProFTPD as required.
When developing websites, place project files in the /opt/lampp/htdocs directory, as this is the root directory for Apache in XAMPP. You may need root privileges to add or edit files in this location. Adjusting permissions can be done with sudo chown -R your-username /opt/lampp/htdocs to allow easier file management without elevated privileges.
To start XAMPP run the following and the command will return a list of running services:
sudo /opt/lampp/lampp start
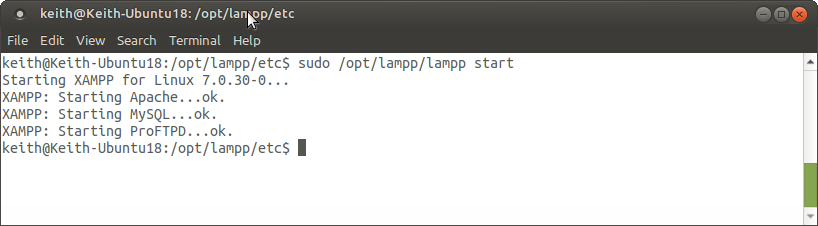
To stop XAMPP run the command below and it will return a list of the stopped services.
sudo /opt/lampp/lampp stop
To restart XAMPP run the command below and it will stop and restart the running services.
sudo /opt/lampp/lampp restart
You can also stop/start/restart individual services by appending “apache”, “mysql” or “ftp” to the end.
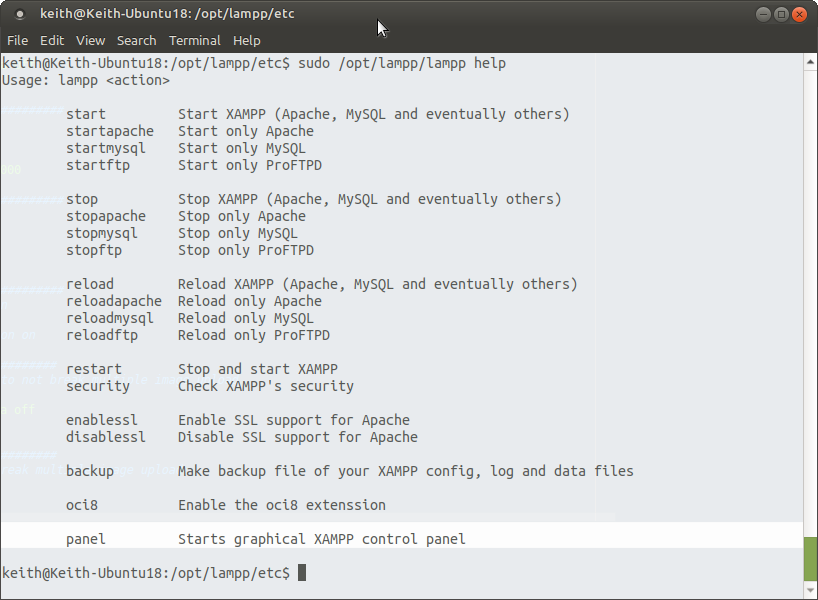
start – Start XAMPP (Apache, MySQL and eventually others)
startapache – Start only Apache
startmysql – Start only MySQL
startftp – Start only ProFTPD
stop – Stop XAMPP (Apache, MySQL and eventually others)
stopapache – Stop only Apache
stopmysql – Stop only MySQL
stopftp – Stop only ProFTPD
reload – Reload XAMPP (Apache, MySQL and eventually others)
reloadapache – Reload only Apache
reloadmysql – Reload only MySQL
reloadftp – Reload only ProFTPD
restart – Stop and start XAMPP
security – Check XAMPP’s security
enablessl – Enable SSL support for Apache
disablessl – Disable SSL support for Apache
backup – Make backup file of your XAMPP config, log and data files
oci8 – Enable the oci8 extenssion
panel – Starts graphical XAMPP control panel
Finally, to uninstall XAMPP, run sudo /opt/lampp/uninstall and then manually remove the /opt/lampp directory if required. This outline should allow you to set up and use XAMPP on Ubuntu effectively for local development purposes.
December 2024
In an era where digital privacy concerns are at the forefront of online discourse, many organisations are reassessing their tools to ensure compliance with data...
→ Continue reading"Simple Analytics: A privacy-focused alternative to Google Analytics"
November 2024
In today’s digital world, protecting your privacy online has become essential. With personal data constantly being shared, stored, and potentially accessed by unauthorised parties, safeguarding...
→ Continue reading"Simple steps to protect your privacy online"
November 2024
Making the most of Bluesky after coming from whatever Twitter (𝕏) has become involves exploring the platform's unique features, adapting to its smaller, community-driven culture,...
November 2024
With the increasing dependency on web applications in daily operations, securing these applications is paramount to safeguarding data and protecting against breaches. This blog post...
October 2024
Cookieless website tracking is a method of collecting analytics data and monitoring website behaviour without the need for traditional browser cookies. Traditionally, cookies have been...
→ Continue reading"Cookieless website tracking and analytics"
October 2024
The disagreement between WordPress and WP Engine has sparked considerable debate within the WordPress community and could have important implications for users of the WordPress...
→ Continue reading"What's going on between WordPress and WP Engine?"